Today, blockchains are eminent in cryptocurrency systems worldwide. While blockchain initially focused on Bitcoin, the technology gave birth to newer cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum, Litecoin, and Stellar Lumen.
Cardano is a blockchain network conceived as a sustainable and scalable decentralized application (DApp) development platform with verifiable smart contracts. Emphasizing the Cardano blockchain, this article highlights Cardano and the advantages of deploying blockchain networks on a public cloud platform like the GCP.
What is Cardano?
Launched in 2017, Cardano is an open-source, proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain network, and ADA is the coin powering this network. Created by Charles Hoskinson, one of the co-founders of Ethereum, Cardano’s goal is to improve upon its alternatives like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Thus, Cardano aimed to solve its predecessors’ issues by working on three main elements – scalability, interoperability, and sustainability.
Cardano’s USPs
The Cardano project drives decision-making from scientific philosophy and peer-reviewed academic research. As a result, Cardano promises certain vital features like the option to send money in different currencies and a system for fund allocation.
Cardano also solves shortcomings like high transaction fees and lack of liquidity.
Not merely another cryptocurrency, Cardano is a platform for developers to build smart contracts and create decentralized applications.
Introducing the PoS (Proof of Stake)
A unique feature of the Cardano network is a consensus mechanism called PoS (Proof of Stake). PoS signifies that instead of mining, Cardano uses staking, a process where participants, or “validators,” deposit set amounts of ADA to earn participation in the blockchain operation.

Further, users can become full node validators or delegate their stake to other users to validate transactions on the network.
In contrast, Bitcoin and Ethereum run on the Proof of Work consensus mechanism, which requires large amounts of processing power. Consequently, members of the network, or “miners,” expend effort in solving an arbitrary mathematical puzzle for validating transactions and mining new tokens.
The Proof of Stake mechanism was created as an alternative to this method to overcome these shortcomings.
On a side note, Ethereum is closer to shifting to the Proof of Stake consensus mechanism to become more energy-efficient and allow for better scalability.
Cardano Advantages
Here are some ways that Cardano edges over other blockchain platforms:
- System Design
Cardano promotes system design using pure functions. As a result, individual components are easily testable while in isolation. Cardano runs on Haskell – thus, offering a robust code execution process including test simulations and powerful techniques for optimizing & correcting code. - Security
Ouroboros – which is Cardano’s PoS (Proof of Stake) protocol promotes reliable security measures. The security regimes are a result of numerous peer-reviewed academics. - Energy Efficiency
The PoS protocol consumes much lesser energy and computational power. As a result, Cardano’s proof of stake blockchain is less resource intensive and cleaner for the environment. - Decentralization
Cardano’s backbone comprises nearly 3,000 distributed stake pools – which are community operated. There’s no dependency on a central authority for validations of any blocks and transactions. - Seamless Upgrades
Conventionally, blockchain upgrades feature hard forks. During a hard fork, the existing protocol halts operations; While the new configurations are implemented, the entire blockchain essentially restarts and erases all previous history.
Cardano offers a hard-fork combinator feature that ensures smooth transitioning into a new protocol. Additionally, Cardano also saves history of previous blocks to ensure a seamless and disruption-free experience for end users.
DApps Fueled by Smart Contracts
The two real-world applications of the Cardano blockchain include the ADA cryptocurrency and decentralized apps, or DApps.
While ADA is the native cryptocurrency of the Cardano blockchain, DApp is a decentralized application that uses blockchain technology. ADA and DApp aren’t governed by a single entity and can run autonomously when predetermined conditions are fulfilled through ’smart contracts.’
What is a Smart Contract?
Smart Contracts are programs stored on a particular blockchain that act as digital agreements, or guarantees, between two parties. These transactions or agreements get executed automatically; however, it only happens upon meeting certain prerequisite conditions.
One of the most significant advantages of smart contracts is the lack of involvement of individuals or intermediaries. Since the agreement details remain on a decentralized blockchain, smart contracts offer greater transparency and traceability.
Types of Smart Contracts
Broadly, there are two kinds of smart contracts – financial contracts or building programs (DApps).
A financial contract deals with the communication and representation of values between parties. DApps feature a smart contract: a piece of code that allows a decentralized system to operate.
Smart Contract Applications
While the Ethereum blockchain has been the dominant host for DApps and smart contracts, Cardano’s smart contracts will follow a similar model. Moreover, programmers for these smart contracts will use one of two languages: Plutus or Marlowe. While the former is a platform to write full applications that interact with the Cardano blockchain, the latter is a domain-specific language.
An example of Cardano’s smart contracts includes the Alonzo hard fork, launched in September 2021. These smart contracts allow the creation of DApps on Cardano, thus opening up a variety of potential uses for the blockchain system. Further, organizations can use smart contracts for financial transactions, insurance, property ownership, and records.
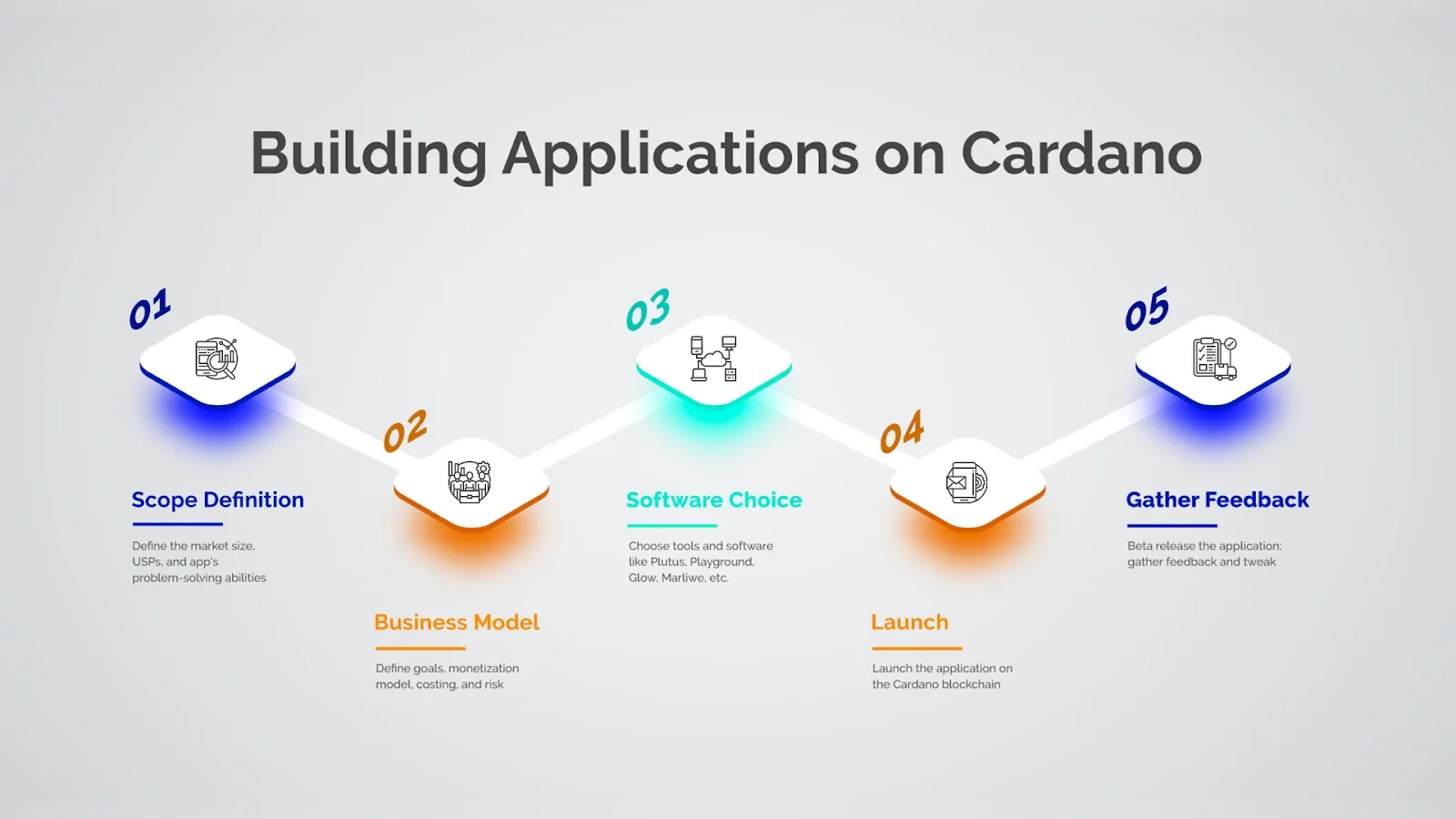
How to Build Applications Using Cardano?
Cardano is an effective blockchain platform for building smart contracts, websites, and apps. Here’s how applications get developed on Cardano:
- The first step before building an application on Cardano involves defining its scope. This includes analyzing the app’s problem-solving abilities, market size, and potential competitors.
- Next, it’s critical to define the app’s business goals and determine the optimum monetization model. This step would involve chalking out details like the methods of revenue generation, budget requirements and weighing any potential risks.
- Now, the app developers must choose the best-suited professional tools and software. This choice would influence the actual development stage and the selection of standard software or specialized solutions like Plutus, Playground, Glow, Marlowe, etc.
- The final stage is launching and testing the application on the Cardano Blockchain.
One renowned instance of a decentralized app built within the Cardano ecosystem is Empowa. The project seeks to address the severe shortage of affordable housing in Africa and the consequent poverty cycle. From a technical perspective, Empowa aims to use blockchain and DeFi to provide decentralized financing for new, affordable property and organize the building work. Most important, Empowa is an example of a project that aims to take advantage of modern building technology while prioritizing sustainability.
Other applications built using Cardano include – MELD, a DeFi, non-custodial banking protocol that builds applications on the Cardano blockchain to securely lend and borrow crypto and fiat currencies. Another application is Ardana: a comprehensive stablecoin hub built to integrate with the Cardano network.
Blockchain Development Fueled by Google Cloud
Cloudification is the next big thing in technology. Massive organizations are rapidly moving to cloud-based servers for hosting and deploying applications.
Interestingly, even blockchains firms are steadily migrating to the cloud.
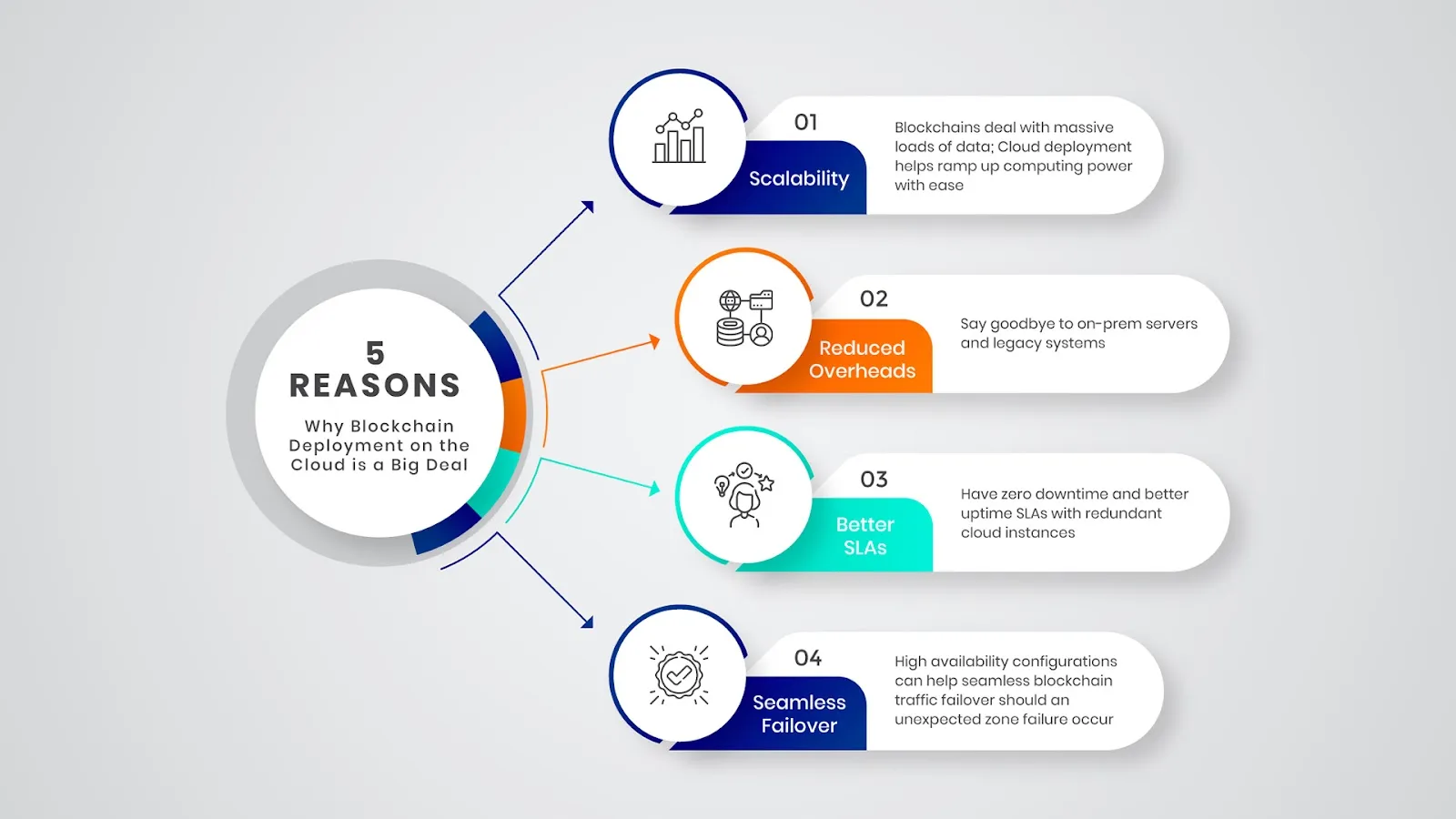
Why Cloud Deployment is a Big Deal for Blockchain
Blockchain companies deal with massive silos of data. Blockchains depend on 1000s of nodes, and new nodes get constantly added. As a result, blockchain companies require significant aggregate computer power.
Scalability is also quite crucial. Blockchains must exhibit agility in quickly ramping up computer power as and when the network grows.
The old-school way of app deployment involves investing and managing legacy on-prem servers. However, on-prem servers are pretty inefficient and time-consuming. Consequently, blockchain businesses leverage cloud computing services for hosting.
Insight: Blockchain networks enable organizations to utilize a distributed ledger for securely transacting and sharing data.
Computing power is an enormous cost in the blockchain world. Switching to the cloud enables developers to add computer power with ease.
Additionally, uptime SLA is an essential metric for blockchain enterprises. Zero downtime helps blockchain networks to generate revenue round the clock. As a result, redundancy is the need of the hour: having access to a distributed global cloud infrastructure.
High availability configurations can help seamless blockchain traffic failover should an unexpected zone failure occur.
Why GCP is the Real Gem for Blockchain Development
The GCP (Google Cloud Platform) offers GKE (Google Kubernetes Engine) – which is essentially a managed environment for managing, deploying and scaling containerized applications.
Upon leveraging the GKE cluster services, here are some unparalleled benefits you can reap:
- Automated scaling of node instances
- Auto repair for proactive health checks and increased uptime of node instances
- Auto upgrades of node software
- Inter cluster node pools for smart workload distribution
A blockchain is made up of several blocks or nodes – and utilizing a service like GKE helps scale your network seamlessly.
The above benefits clearly highlight why GKE powered by GCP is the optimum choice for hosting blockchain applications.
Building Cardano Apps on GCP
Cardano is open source and offers a unique set of micro services that interact with each other. Moreover, Cardano also houses a persistent database. As a result, GKE is the ideal choice – given its set of automated upgrades and healing perks.
An evolving blockchain app increases the number of microservices running on a cluster. Consequently, the CI/CD pipeline handling becomes a hassle. GKE helps navigate this challenge of constant addition of new images and templates.
Several organizations are migrating to the Google Cloud Platform for application deployment. What are the potential ramifications of such a move?
- Approximate 30% savings by replacing the legacy database layer, thus reducing operational overheads
- Seamless scalability for handling peak network loads
- Enhanced flexibility for testing code against production data
- Frictionless security settings and policies
Combine GCP with other managed services like Google Cloud Spanner and Compute Engine, and you have a complete powerhouse packed with fascinating features for blockchain business to scale and dominate.
Blockchain Businesses Building with D3V
Migrating to GCP is one thing – designing an efficient and tailor-made cloud migration strategy is a whole different ball game.
The future has many scintillating blockchain applications like supply chain traceability, retail loyalty rewards, real estate transactions, and digital voting. Not only is Blockchain here to stay, in future efforts we expect to see more blockchain tools offered as a SaaS product on public cloud providers.
Stay ahead of the curve – if you’re contemplating a cloud migration for your blockchain services, reach out to D3V for a free technical consultation.


